Technology addiction is one of the most talked‑about behavioral health issues. New data show that more people than ever struggle with compulsive use of digital tools, from smartphones to social media to video games, and the impact spans personal, academic, and workplace life. For example, over 210 million people worldwide are estimated to be addicted to social media and internet use, with about 33 million of those in the U.S. alone.
In industry settings, employers are noting that excessive digital engagement correlates with reduced job performance, while educators are concerned about rising screen addiction among students affecting academic outcomes. From mental health clinics to schools and workplaces, tracking these trends helps shape prevention and support strategies. Explore the statistics below to understand how technology addiction is evolving globally and within the United States this year.
Editor’s Choice
- 210 million people worldwide are estimated to be addicted to social media and internet use in 2025.
- Around 10% of Americans (≈33 million people) were addicted to social media in 2025.
- 21.8% of internet users globally exhibit moderate to severe internet addiction.
- Over 1.58 billion people globally are estimated to experience some level of smartphone addiction in 2025.
- 57% of Americans report feeling addicted to their phones.
- Teen smartphone separation anxiety is reported by 71% of U.S. teens.
- Daily U.S. adult screen time averages 7.6 hours, with social media nearly 2.8 hours.
Recent Developments
- Internet addiction rates continue climbing globally, with 21.8% of users exhibiting moderate to severe addiction in 2025.
- Social media addiction estimates hit 210 million people worldwide this year.
- U.S. social media addiction prevalence remains near 10% of the population.
- 88.6% of Americans check their phones within the first 10 minutes of waking.
- American adults report being checked on average 144 times per day.
- Teen screen separation anxiety, 71% feel irritable without their device.
- Global smartphone addiction rose 7.4% from the previous year.
- Excessive social media use is associated with negative emotions in young adults.
Global Trends in Technology Addiction Prevalence
- An estimated 210 million people worldwide were addicted to social media and related internet use in 2025.
- About 4.69% of all global social media users show addiction‑like behaviors.
- 21.8% of global internet users show moderate to severe internet addiction.
- Global smartphone addiction affects more than 1.58 billion people.
- Internet use disorder prevalence averages around 6% globally among some age groups.
- Meta‑analyses indicate internet addiction rates vary significantly across regions.
- Social media addiction rates differ by culture and access to technology.
- Regions such as Africa and Asia report higher average addiction rates than some Western countries.
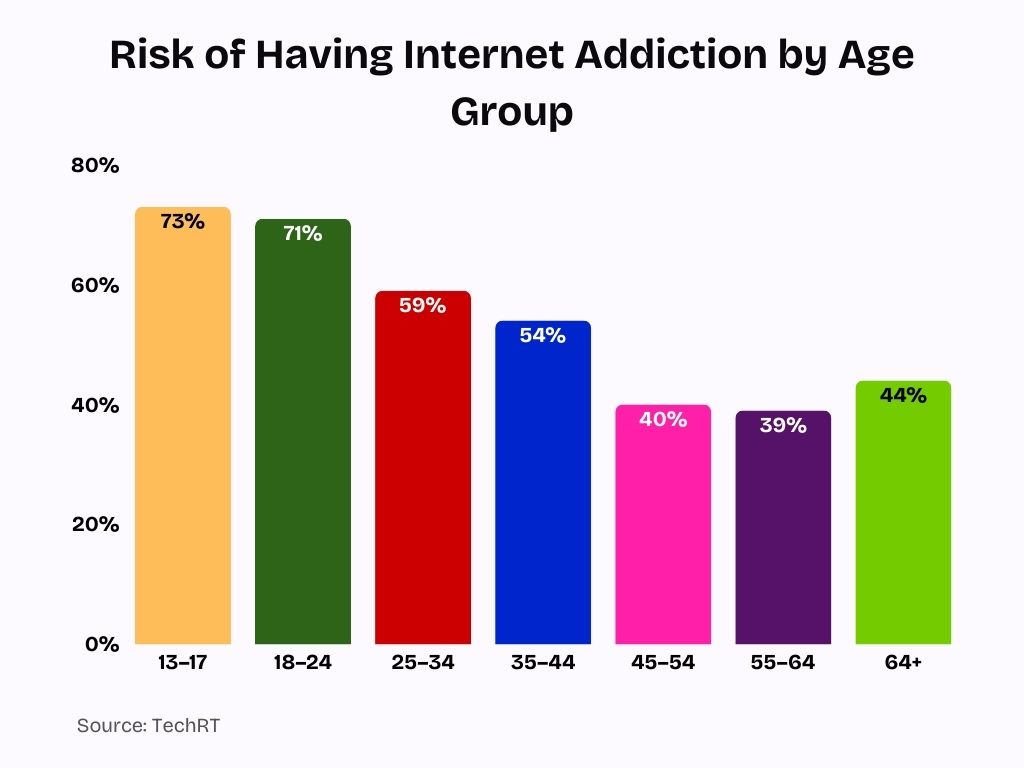
Internet Addiction Risk by Age Group
- Teenagers (13–17) show the highest risk, with 73% at risk of internet addiction, highlighting early exposure and heavy digital reliance.
- Young adults (18–24) follow closely, with 71% risk, driven by social media, gaming, and streaming habits.
- Adults aged 25–34 report a 59% risk, reflecting increased dependence on the internet for work, entertainment, and communication.
- Middle-aged adults (35–44) face a 54% risk, showing that internet addiction extends well beyond younger demographics.
- Adults aged 45–54 see a sharp decline in risk to 40%, indicating more balanced internet usage patterns.
- Older adults (55–64) record the lowest risk at 39%, suggesting greater digital self-regulation.
- Seniors aged 64+ still show a notable 44% risk, proving internet addiction is not limited to youth.
Children and Teens Affected by Technology Addiction
- Around 11% of adolescents exhibit problematic social media behavior globally.
- 50.4% of teens aged 12–17 report 4+ hours daily screen time, exceeding pediatric recommendations.
- 27.1% of high screen time teens experience recent anxiety symptoms, versus 12.3% with less.
- Girls show higher problematic social media use at 13%, compared to 9% in boys.
- 8.5% of children and teens under 18 worldwide display gaming addiction signs.
- 12% of adolescents risk problematic gaming, with boys at 16% versus 7% girls.
- 65% of U.S. children aged 6–12 use screens over 3 hours daily, excluding school.
- 41% of heavy social media teens rate their mental health as poor or very poor.
- 15.1% prevalence of internet addiction was found among high school adolescents.
Workplace Performance and Technology Addiction Impact
- 30% of Americans say they would be more productive without their smartphones while working, indicating that distraction significantly impacts workplace output.
- Multitasking between phone use and work tasks has been shown to reduce productivity by up to 40% for employees.
- On average, U.S. workers check their devices 352 times per day, contributing to task interruptions and performance dips.
- A self‑reported study found a moderate link between smartphone addiction and lowered productivity in work settings.
- 3 in 10 American workers admit their phones affect job performance.
- Excessive social media browsing during work hours correlates with inattention and slower task completion.
- Professionals using phones for browsing or non‑work tasks lose significant focus periods per shift, as reported in workplace behavior surveys.
- Employers increasingly note that frequent notifications and app switching contribute to cognitive fatigue and errors.
Smartphone Usage as a Driver of Technology Addiction
- Over 1.58 billion people globally are estimated to experience some form of smartphone addiction in 2025, a 7.4% increase from last year.
- 71% of U.S. teens report feeling anxious or irritable when separated from their phones for more than 30 minutes.
- On average, adults check their phones 352 times per day, or about once every 2.7 minutes.
- Globally, about 48% of people are considered addicted to their phones, with 50% of teens saying they’re addicted.
- 87% of people check their phones within an hour of waking or before bed, habits that can disrupt routines and sleep.
- Excessive smartphone use is linked to higher levels of anxiety and depression, especially in younger users.
- Frequent checking behavior (every few minutes) is associated with lowered productivity and increased stress.
- Screen disruptions from smartphone usage are tied to poorer academic and work outcomes.
Regional Differences in Technology Addiction Statistics
- Social media addiction rates vary globally from 5% to 31% across 32 countries.
- In Africa, internet addiction prevalence reaches 44.6% in Northern regions.
- Sub-Saharan Africa shows 31% internet addiction rates among populations.
- In Asia, young adults have 61.4% smartphone addiction.
- China reports 13.8% internet addiction among college students.
- India sees high addiction, with only 8% of parents reporting no child addiction.
- European adolescents average 11% problematic social media use, up from 7%.
- Romania leads Europe at 22% problematic social media use among youth.
- US social media addiction stands at 10%, affecting 33 million people.

Social Media Use and Its Link to Technology Addiction
- Around 210 million people worldwide show clinical signs of social media addiction in 2025.
- In the U.S., roughly 10%–14% of adults may be addicted to social media platforms.
- Up to 36% of teens self‑identify as spending “too much time” on social media.
- 48% of teens say social media has a mostly negative effect on their peers’ well‑being, up from 32% in 2022.
- Social media use is linked to stress, anxiety, and depressive symptoms in young adults.
- Over 60% of U.S. college students report addictive social media use.
- About 82% of Gen Z adults acknowledge dependence on social media apps.
- Increased social media use often aligns with negative self‑perception and social comparison.
Online Gaming Behaviors and Technology Addiction Risks
- Global prevalence of Internet Gaming Disorder reached 6.7% in 2025, with adolescents particularly affected.
- Among teen gamers, 8.9% in the U.S. meet clinical criteria for gaming addiction.
- 18.6% of adolescent males show clinically significant gaming addiction symptoms worldwide.
- Average daily playtime among gaming addicts exceeds 5 hours.
- MMORPGs and battle royale games are common in extended sessions tied to addictive patterns.
- Asian regions report higher gaming disorder prevalence than many Western nations.
- Extended gaming correlates with lower academic performance for some youth.
- Gaming addiction risk increases when combined with social media and smartphone overuse.
Streaming and Entertainment Habits Fueling Technology Addiction
- 98% of global web access comes from mobile, and 97.8% from smartphones, showing where entertainment consumption is centered.
- Video and media streaming dominate mobile usage, with 92% of users watching on phones.
- Entertainment platforms are a major driver of prolonged screen sessions linked to compulsive behavior.
- Binge streaming can displace offline social and physical activities, increasing the risk.
- Streaming addiction often overlaps with social media and gaming patterns, amplifying overall screen dependency.
- Users under 25 spend significantly more time watching online content than older adults.
- A strong correlation exists between mobile streaming habits and disrupted sleep cycles.
- Excessive video consumption is tied to reduced real‑world engagement and productivity loss.
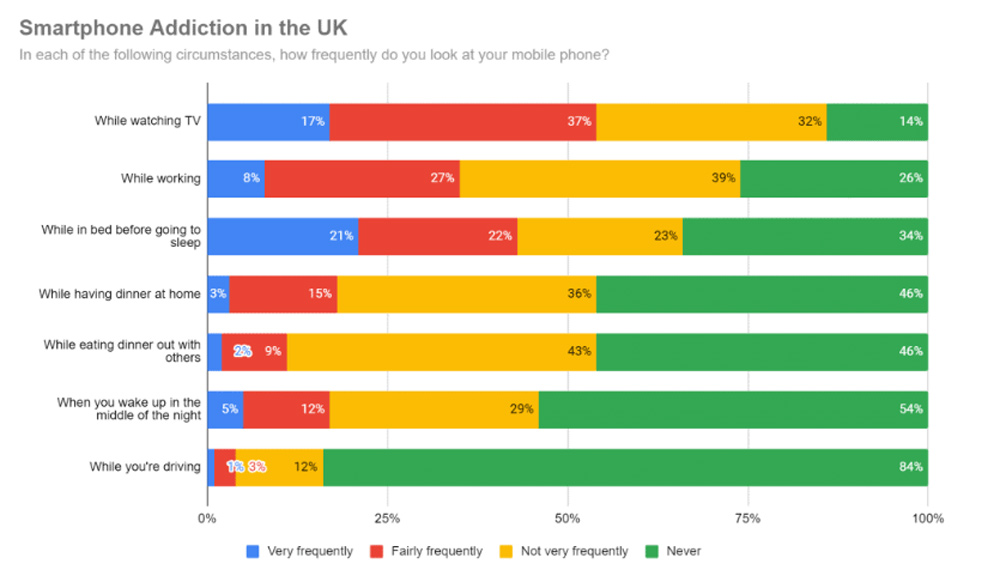
Smartphone Addiction in the UK
- Watching TV fuels frequent phone use, with 54% of people checking their smartphones very or fairly frequently, showing strong second-screen behavior.
- Workplace distraction is significant, as 35% admit to checking their phones frequently while working, potentially impacting focus and productivity.
- Bedtime smartphone habits are deeply ingrained, with 43% using their phones frequently before sleep, a behavior linked to poor sleep quality.
- Dinner at home is less affected, yet 18% still check their phones frequently, indicating growing digital intrusion into family time.
- Social dining sees lower usage, with 89% saying they use phones not very frequently or never when eating out with others.
- Night-time phone checking remains common, as 46% look at their phone after waking in the middle of the night, disrupting rest cycles.
- Driving shows the strongest self-control, with 84% saying they never check their phone while driving, though 4% still admit to frequent use.
- Context strongly shapes phone behavior, with leisure moments like TV and bedtime seeing the highest addiction signals, while high-risk activities show greater restraint.
Mental Health Outcomes Related to Technology Addiction
- Teens with problematic smartphone use are twice as likely to experience anxiety and nearly three times as likely to experience depression.
- 18.7% of older teens and 14.5% of younger teens report problematic smartphone use.
- 1-week social media detox reduces anxiety by 16.1%, depression by 24.8%, and insomnia by 14.5%.
- Teens with high addictive screen use face over twice the risk of suicidal behaviors compared to low-use peers.
- 23.3% median prevalence of problematic smartphone use among youth, linked to depression (OR 3.17).
- Smartphone addiction correlates with depression (r=0.375), anxiety (r=0.253), and stress (r=0.328).
- Moderate-to-high problem technology use raises high life stress odds by 2.04× and low self-esteem odds by 2.08×.
- 67% of teens lose sleep due to late-night smartphone use, worsening mental health.
- 48.1% of young adults show moderate internet addiction, tied to depression, anxiety, and sleep issues.
- Smartphone addiction correlates with negative emotions (r=0.332) and lower life satisfaction.
Disrupted Sleep Patterns from Technology Addiction
- Adolescents with internet addiction face a 54.86% insomnia rate.
- 68% of young adults with smartphone addiction report poor sleep quality.
- Over 70% of adolescents have 2+ devices in their bedrooms at night.
- 90% of studies link screen media to delayed bedtime and shorter sleep.
- 39% of young adults exhibit smartphone addiction tied to sleep issues.
- 65.7% of bedtime blue light users perceive sleep disturbances.
- 26.3% of high schoolers get 6 hours or less of sleep due to devices.
- 48.8% of students using devices pre-bed have poor sleep quality.
- Internet addicts are 2.2 times more likely to have sleep problems.
- 35.3% of nightly device users experience poor sleep quality.
-
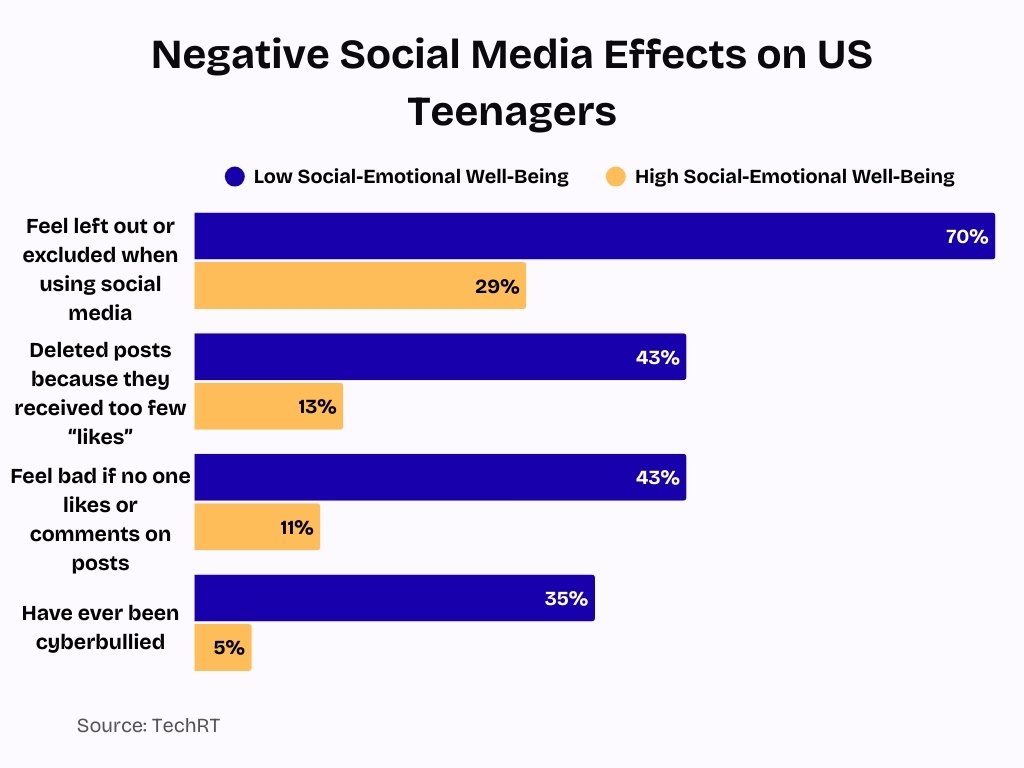
Negative Social Media Effects on U.S. Teen Emotional Well-Being
- Teens with low social-emotional well-being are far more vulnerable to negative social media experiences across every metric measured.
- 70% of teens with low emotional well-being say they feel left out or excluded when using social media, compared to just 29% among those with high well-being.
- Engagement pressure is significantly higher for emotionally vulnerable teens, with 43% deleting posts due to too few “likes,” versus only 13% of teens with high well-being.
- The emotional impact of validation is stark: 43% of teens with low well-being feel bad about themselves if their posts receive no likes or comments, compared to 11% among emotionally healthier peers.
- Cyberbullying disproportionately affects vulnerable teens, as 35% of those with low emotional well-being report being cyberbullied, versus just 5% of teens with high well-being.
Academic Challenges Connected to Technology Addiction
- A 2025 university study found 37.1% of students met criteria for technology addiction, and these students were 21% more likely to show low academic performance than non‑addicted peers.
- Adolescents with >3 hours of daily screen time had mean grades around 62.1%, compared with 88.4% among those with almost no screen use.
- A large adolescent study reported that higher screen time was moderately associated with decreased academic performance and poorer sleep, both of which predicted lower GPA scores.
- Research on internet use and cognition shows that heavy online media multitasking can cause significant drops in sustained attention test performance, impairing students’ ability to focus in class.
- Neuroimaging work indicates that frequent internet use is linked to reduced development of brain regions supporting executive functions and verbal intelligence over 3 years, which can undermine learning.
- A study of school‑going youth reported that smartphone and internet‑addicted students had lower academic success and higher fatigue levels than peers with little or no addiction symptoms.
- Evidence on early adolescents shows that more screen time is tied to worse mental health, more behavioral problems, and lower academic performance, especially when combined with short sleep.
- A systematic review of university students reports that internet‑addicted learners frequently show reduced attentional focus, more memory consolidation difficulties, and declining overall academic functioning.
- Inferential statistics from a 500‑student sample found a significant relationship between internet addiction scores and poorer academic achievement (chi‑square 20.11, p<0.01).
Reduced Job Productivity Due to Technology Addiction
- Employees lose up to 122 hours annually refocusing after digital distractions.
- Notifications cause task switches, costing 23 minutes to recover focus each time.
- Cell phones account for 55% loss in work productivity due to distractions.
- 70% of employees report that social media distractions reduce concentration and task efficiency.
- Smartphone addiction correlates moderately with self-reported productivity decreases at work.
- 27% of task-switches from alerts lead to over 2 hours lost before resuming original tasks.
- Technostress links to lower task completion rates and reduced work quality.
- Remote workers experience an 8-19% productivity drop from digital interruptions and coordination issues.
- 79% of workers get distracted within an hour, slashing sustained focus.
- 40% decrease in productivity from excessive smartphone use and cognitive overload.
Social Isolation Stemming from Technology Addiction
- Teens spending heavy time on screens report 25.9% depression rates vs. 9.5% for low screen time.
- 95% of teens now own smartphones, up from 23% in 2011, correlating with rising loneliness.
- Phubbing shows a r=0.492 correlation with media addiction, weakening relationship quality.
- Social isolation directly predicts smartphone addiction, mediated by loneliness (r=0.583 to 0.69).
- One in 6 people worldwide is affected by loneliness, with the highest rate in 13-17-year-olds at 20.9%.
- 62% of observed individuals use devices during face-to-face presence, reducing interactions.
- Mobile dependency and social withdrawal show a strong r=0.78 positive correlation in children.
- 35% of the population has internet addiction; up to 60% teens show cell phone addiction signs.
- Global social isolation prevalence rose 13.4% from 2009-2024 to 21.8%.
- Social media addiction correlates with r=0.434 with loneliness and reduced offline support.
Compulsive Internet Use and Technology Addiction Overlap
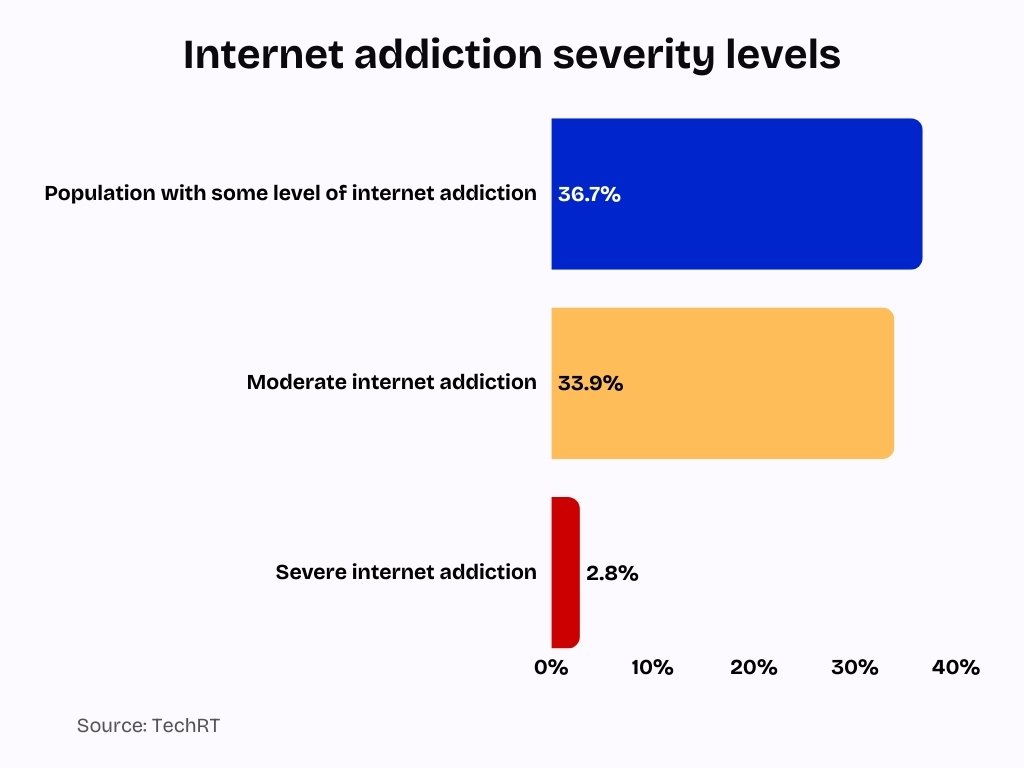
- Approximately 36.7% of the global population experienced some level of internet addiction in 2025.
- 33.9% show moderate internet addiction symptoms, and 2.8% severe.
- Internet addiction often co‑occurs with social media and gaming addiction patterns.
- Compulsive online behaviors may replace offline social activities.
- Problematic internet use predicts lower academic and workplace functioning.
- Many compulsive users report difficulty disconnecting even during personal time.
- Internet addiction tends to peak in adolescence and early adulthood.
- High internet dependency aligns with anxiety, sleep issues, and attention challenges.
Recovery Efforts and Support for Technology Addiction
- Digital detox programs achieve a 91% improvement rate in participant well-being.
- CBT shows 42% response and 36% remission rates for addictions.
- Screen limiters enable 95% of users to save over 2 hours daily.
- Peer support groups expand digital wellness engagement significantly.
- School programs cut digital overuse with a d = 1.47 effect size.
- 58% of private plans cover behavioral health treatments.
- Family therapies boost recovery when paired with medications.
- Mindfulness interventions reduce mobile addiction substantially.
Emerging Trends Shaping the Future of Technology Addiction
- Around 26.99% of people globally meet criteria for smartphone addiction, with 17.42% for social media and 14.22% for internet gaming, underscoring rising tech dependence.
- AI-optimized feeds in social platforms are explicitly designed to maximize screen time, deepening reward-center activation and reinforcing addictive use patterns in teens.
- One global estimate suggests more than 210 million people suffer from social media and internet addiction, highlighting the scale of technology overuse.
- Teens now average about 8 hours of daily screen time, with up to 60% showing signs of problematic or addictive smartphone use.
- In young adults aged 18–22, about 45% self-report technology addiction, including 5% who say they are definitely addicted.
- A mobile neurofeedback trial in children at risk of internet addiction reported significant improvement in addiction scores after a 3‑month intervention.
- Real-time fMRI neurofeedback for problematic internet gaming showed participants could downregulate reward-related brain activity after just 2 sessions, indicating potential for tech-addiction therapies.
- A meta-analysis of EEG neurofeedback found a large effect size (Hedges’ g = 0.85) in reducing addiction symptoms, supporting its promise for behavioral and tech-related addictions.
- Clinical and observational research links AI-driven dopamine feedback loops with higher rates of compulsive social media use and reduced intrinsic motivation in frequent users.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What percentage of the global population is estimated to be addicted to the internet?
About 36.7% of the global population experiences some level of internet addiction, including 33.9% moderate and 2.8% severe cases in recent studies.
How many people worldwide are believed to be addicted to social media?
An estimated 210 million people worldwide are considered addicted to social media and internet platforms.
What share of U.S. adults admit to being addicted to their phones?
Approximately 56.9% of American adults self‑report that they are addicted to their smartphones.
What percentage of global smartphone users meet clinical criteria for smartphone addiction?
About 21% of global smartphone users meet clinical criteria for behavioral addiction to their devices as of 2025.
What percentage of adolescents show signs of problematic social media use?
More than 11% of adolescents show signs of problematic social media behavior, according to WHO data.
Conclusion
Technology addiction clearly exceeds casual concern; it’s reshaping sleep, academic achievement, workplace efficiency, and social dynamics across age groups. Data show disrupted sleep patterns and sleep quality issues directly linked to digital overuse, while excessive screen time connects with declines in school performance and job productivity. At the same time, patterns of social withdrawal and isolation raise flags for broader well‑being. Recovery strategies like digital detox and therapeutic interventions are expanding, yet emerging trends suggest both challenges and opportunities ahead as society continues to adapt to pervasive technology use. Addressing this issue will require coordinated efforts across families, schools, workplaces, and health systems to promote balanced digital engagement and long‑term wellness.



Leave a comment
Have something to say about this article? Add your comment and start the discussion.